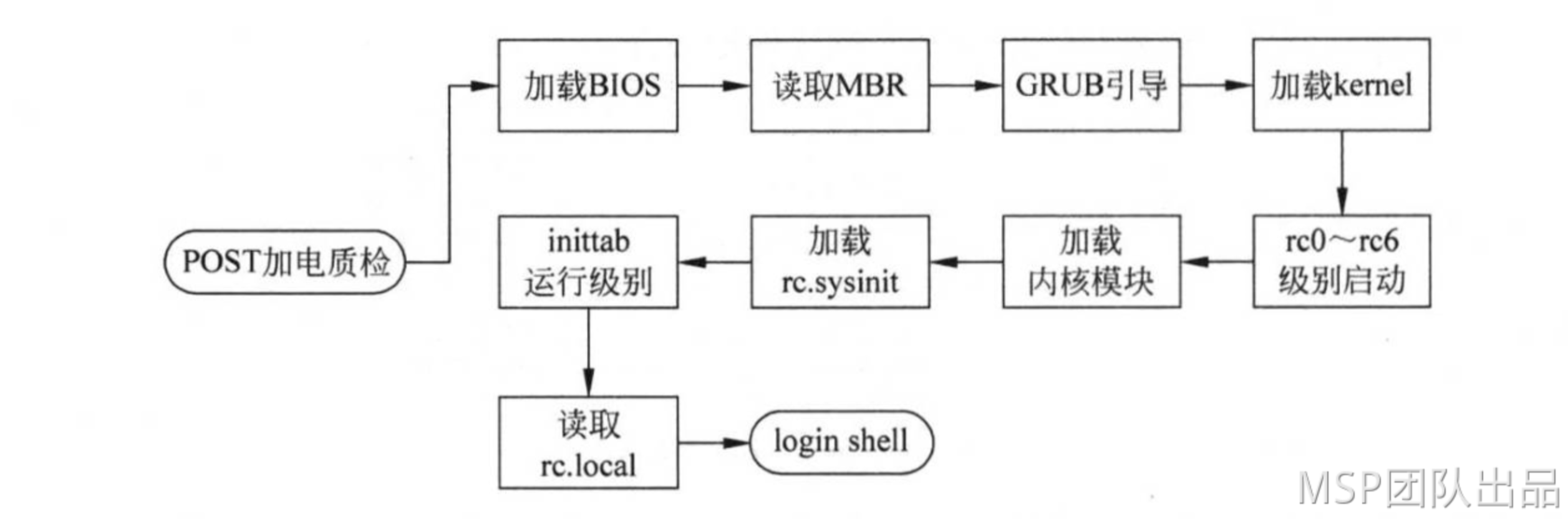
PostgreSQL 锁等待排查
在数据库中,常用 锁 和 MVCC 来保障事务的一致性及提高并发性。锁问题的定位和排查也是数据库运维人员必会的技能,本篇文章介绍 PostgreSQL 如何排查定位锁堵塞问题。
1. PostgreSQL 的锁
这里推荐阅读官方文档,
2. 死锁问题
如果业务逻辑设计不慎,可能导致严重的锁等待,或者死锁的产生。PostgreSQL 自动检测死锁情况并会自动回滚其中一个事务进行处理,从而其他事务提交。请看下方 Case:
postgres= select * from pgbench_accounts where aid in (3, 4, 5);
aid | bid | abalance | filler
-----+-----+----------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3 | 1 | 0 |
4 | 1 | 0 |
5 | 1 | 0 |
(3 rows)
| 事务一 | 事务二 |
|---|---|
| begin; | begin; |
| update pgbench_accounts set abalance = 1 where aid = 3; | update pgbench_accounts set abalance = 1 where aid = 4; |
| - | update pgbench_accounts set abalance = 1 where aid = 3; -- 被堵塞 |
| update pgbench_accounts set abalance = 1 where aid = 4; | update 执行成功 |
| commit -- 自动 rollback | commit; |
ERROR: deadlock detected DETAIL: Process 127589 waits for ShareLock on transaction 702; blocked by process 127570. Process 127570 waits for ShareLock on transaction 701; blocked by process 127589. HINT: See server log for query details. CONTEXT: while updating tuple (0,4) in relation "pgbench_accounts"
PostgreSQL 有自动死锁检测机制,和 MySQL 相同检查到死锁后,如果大于锁超时时间,会自动回滚其中一个事务,默认为 1s:
select current_setting('deadlock_timeout');MySQL 可以通过 show engine innodb status 获得历史死锁信息,关于 PostgreSQL 可以通过参数控制log_lock_waits 参数将死锁信息输出到日志中:
2023-07-03 16:39:26.037 CST [127589] LOG: process 127589 detected deadlock while waiting for ShareLock on transaction 704 after 1000.332 ms 2023-07-03 16:39:26.037 CST [127589] DETAIL: Process holding the lock: 14138. Wait queue: . 2023-07-03 16:39:26.037 CST [127589] CONTEXT: while updating tuple (0,4) in relation "pgbench_accounts" 2023-07-03 16:39:26.037 CST [127589] STATEMENT: update pgbench_accounts set abalance = 1 where aid = 4; 2023-07-03 16:39:26.037 CST [127589] ERROR: deadlock detected 2023-07-03 16:39:26.037 CST [127589] DETAIL: Process 127589 waits for ShareLock on transaction 704; blocked by process 14138. Process 14138 waits for ShareLock on transaction 703; blocked by process 127589. Process 127589: update pgbench_accounts set abalance = 1 where aid = 4; Process 14138: update pgbench_accounts set abalance = 1 where aid = 3; 2023-07-03 16:39:26.037 CST [127589] HINT: See server log for query details. 2023-07-03 16:39:26.037 CST [127589] CONTEXT: while updating tuple (0,4) in relation "pgbench_accounts" 2023-07-03 16:39:26.037 CST [127589] STATEMENT: update pgbench_accounts set abalance = 1 where aid = 4; 2023-07-03 16:39:26.038 CST [14138] LOG: process 14138 acquired ShareLock on transaction 703 after 25470.277 ms 2023-07-03 16:39:26.038 CST [14138] CONTEXT: while updating tuple (0,3) in relation "pgbench_accounts" 2023-07-03 16:39:26.038 CST [14138] STATEMENT: update pgbench_accounts set abalance = 1 where aid = 3;
3. 锁问题监控
3.1 pg_stat_activity
该视图是来观测数据库会话的,和 MySQL 中的 processlist 作用相同,也可以通过它观测锁等待:
select pid,
pg_blocking_pids(pid),
wait_event_type,wait_event,
query
from pg_stat_activity;
| Session 1 | Session 2 |
|---|---|
| Begin; | |
| delete from pgbench_accounts where aid = 3; | |
| select * from pgbench_accounts where aid = 3 for update; |
此时 Session 2 被 Session 1 blocking 使用 pg_stat_activity 查询下:
pid | pg_blocking_pids | wait_event_type | wait_event | query
--------+------------------+-----------------+---------------------+----------------------------------------------------------
127589 | {} | Client | ClientRead | delete from pgbench_accounts where aid = 3;
14138 | {127589} | Lock | transactionid | select * from pgbench_accounts where aid = 3 for update;
129038 | {} | | | select pid, +
| | | | pg_blocking_pids(pid), +
| | | | wait_event_type,wait_event, +
| | | | query +
| | | | from pg_stat_activity;
可以看清楚的看到 select...for update 语句被 pid = 127589 的会话堵塞。
3.2 堵塞视图
因为这条 SQL 非常长,使用前建议创建视图,方便后续使用:
create view v_locks_monitor as
with
t_wait as
(
select a.mode,a.locktype,a.database,a.relation,a.page,a.tuple,a.classid,a.granted,
a.objid,a.objsubid,a.pid,a.virtualtransaction,a.virtualxid,a.transactionid,a.fastpath,
b.state,b.query,b.xact_start,b.query_start,b.usename,b.datname,b.client_addr,b.client_port,b.application_name
from pg_locks a,pg_stat_activity b where a.pid=b.pid and not a.granted
),
t_run as
(
select a.mode,a.locktype,a.database,a.relation,a.page,a.tuple,a.classid,a.granted,
a.objid,a.objsubid,a.pid,a.virtualtransaction,a.virtualxid,a.transactionid,a.fastpath,
b.state,b.query,b.xact_start,b.query_start,b.usename,b.datname,b.client_addr,b.client_port,b.application_name
from pg_locks a,pg_stat_activity b where a.pid=b.pid and a.granted
),
t_overlap as
(
select r.* from t_wait w join t_run r on
(
r.locktype is not distinct from w.locktype and
r.database is not distinct from w.database and
r.relation is not distinct from w.relation and
r.page is not distinct from w.page and
r.tuple is not distinct from w.tuple and
r.virtualxid is not distinct from w.virtualxid and
r.transactionid is not distinct from w.transactionid and
r.classid is not distinct from w.classid and
r.objid is not distinct from w.objid and
r.objsubid is not distinct from w.objsubid and
r.pid <> w.pid
)
),
t_unionall as
(
select r.* from t_overlap r
union all
select w.* from t_wait w
)
select locktype,datname,relation::regclass,page,tuple,virtualxid,transactionid::text,classid::regclass,objid,objsubid,
string_agg(
'Pid: '||case when pid is null then 'NULL' else pid::text end||chr(10)||
'Lock_Granted: '||case when granted is null then 'NULL' else granted::text end||' , Mode: '||case when mode is null then 'NULL' else mode::text end||' , FastPath: '||case when fastpath is null then 'NULL' else fastpath::text end||' , VirtualTransaction: '||case when virtualtransaction is null then 'NULL' else virtualtransaction::text end||' , Session_State: '||case when state is null then 'NULL' else state::text end||chr(10)||
'Username: '||case when usename is null then 'NULL' else usename::text end||' , Database: '||case when datname is null then 'NULL' else datname::text end||' , Client_Addr: '||case when client_addr is null then 'NULL' else client_addr::text end||' , Client_Port: '||case when client_port is null then 'NULL' else client_port::text end||' , Application_Name: '||case when application_name is null then 'NULL' else application_name::text end||chr(10)||
'Xact_Start: '||case when xact_start is null then 'NULL' else xact_start::text end||' , Query_Start: '||case when query_start is null then 'NULL' else query_start::text end||' , Xact_Elapse: '||case when (now()-xact_start) is null then 'NULL' else (now()-xact_start)::text end||' , Query_Elapse: '||case when (now()-query_start) is null then 'NULL' else (now()-query_start)::text end||chr(10)||
'SQL (Current SQL in Transaction): '||chr(10)||
case when query is null then 'NULL' else query::text end,
chr(10)||'--------'||chr(10)
order by
( case mode
when 'INVALID' then 0
when 'AccessShareLock' then 1
when 'RowShareLock' then 2
when 'RowExclusiveLock' then 3
when 'ShareUpdateExclusiveLock' then 4
when 'ShareLock' then 5
when 'ShareRowExclusiveLock' then 6
when 'ExclusiveLock' then 7
when 'AccessExclusiveLock' then 8
else 0
end ) desc,
(case when granted then 0 else 1 end)
) as lock_conflict
from t_unionall
group by
locktype,datname,relation,page,tuple,virtualxid,transactionid::text,classid,objid,objsubid ;
还是 2.1 小节,人为制造的锁等待场景,我们使用该视图看看效果:
select * from v_locks_monitor;
-[ RECORD 1 ]-+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
locktype | transactionid
datname | postgres
relation |
page |
tuple |
virtualxid |
transactionid | 705
classid |
objid |
objsubid |
lock_conflict | Pid: 127589 +
| Lock_Granted: true , Mode: ExclusiveLock , FastPath: false , VirtualTransaction: 3/382737 , Session_State: idle in transaction +
| Username: postgres , Database: postgres , Client_Addr: NULL , Client_Port: -1 , Application_Name: psql +
| Xact_Start: 2023-07-03 16:51:06.570461+08 , Query_Start: 2023-07-03 16:51:27.61686+08 , Xact_Elapse: 00:13:38.834827 , Query_Elapse: 00:13:17.788428 +
| SQL (Current SQL in Transaction): +
| delete from pgbench_accounts where aid = 3; +
| -------- +
| Pid: 14138 +
| Lock_Granted: false , Mode: ShareLock , FastPath: false , VirtualTransaction: 4/43636 , Session_State: active +
| Username: postgres , Database: postgres , Client_Addr: NULL , Client_Port: -1 , Application_Name: psql +
| Xact_Start: 2023-07-03 16:56:05.622813+08 , Query_Start: 2023-07-03 16:56:05.622813+08 , Xact_Elapse: 00:08:39.782475 , Query_Elapse: 00:08:39.782475+
| SQL (Current SQL in Transaction): +
| select * from pgbench_accounts where aid = 3 for update;
此视图会按锁的大小排序,要快速解除锁堵塞状态,terminate 最大的锁对应的 PID 即可。
select pg_terminate_backend(127589);
4. 锁相关参数
4.1 deadlock_timeout
默认1s,表示 pg 数据库仅对锁超时大于 1s 的情况进行死锁检测。
4.2 log_lock_waits
默认关闭,若打开该参数则表示会将锁超时超过 deadlock_timeout 的信息记录到日志中。
4.3 lock_timeout
锁等待超时,默认为 0 表示禁用锁超时。若该参数设置 >0 则表示会话等待锁资源 Ns 后如果仍无法获取到相关锁资源则终止相关语句执行。