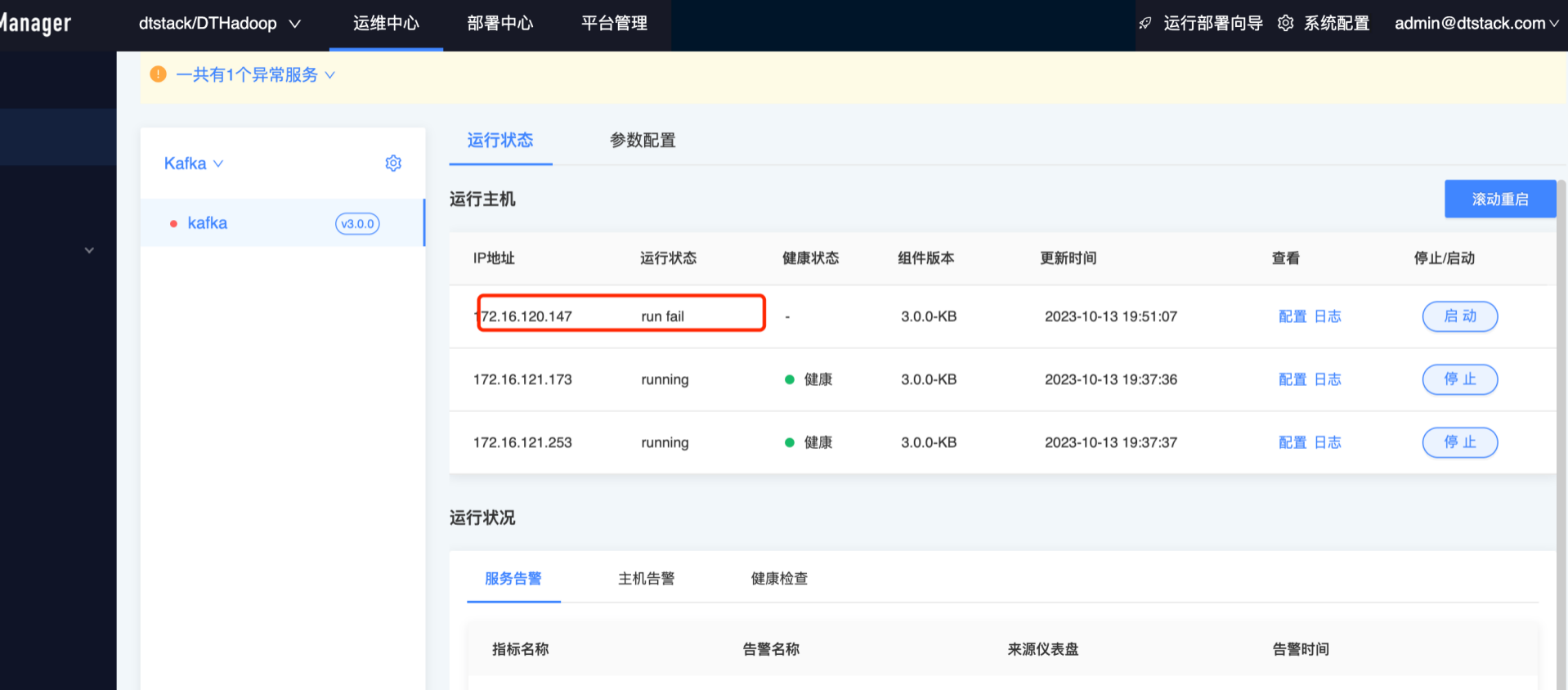
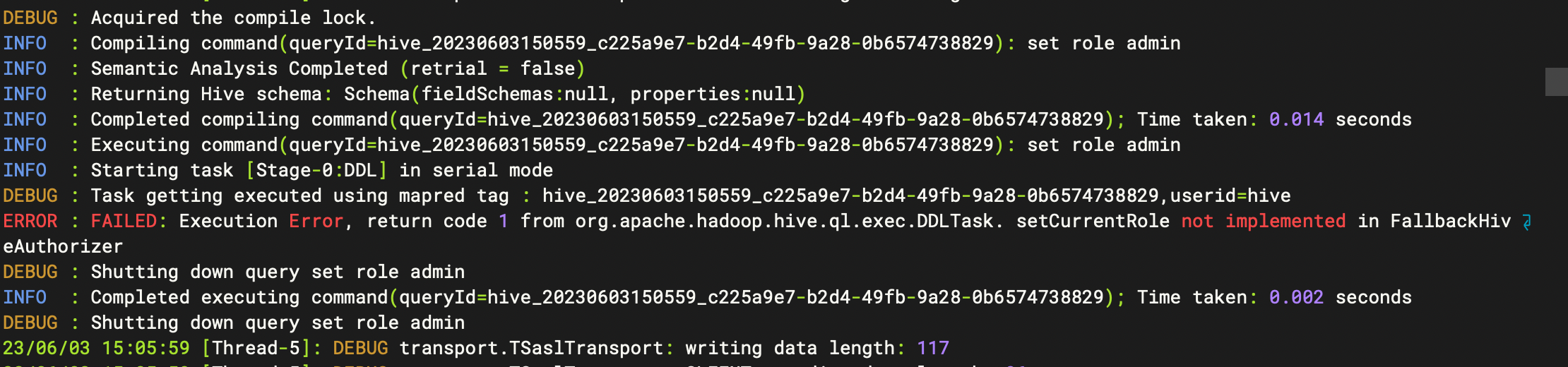
Elasticsearch如何使用内存
ES作为一个JAVA程序,其对内存的使用和管理依赖底层JVM。因而设置内存时需要遵从JAVA的普适原则,如-xmx和-xms设置为相同值等。在JVM的基础上,ES对内存的使用可按功能分为以下几大部分:
1. Segment Memory:
在ES中数据存储都存储为segment。segment是一个完备的lucene倒排索引,通过词典 (Term Dictionary)到文档列表(Postings List)的映射关系,实现快速检索。 由于词典的size会很大,全部装载到内存中不现实,因此Lucene为词典做了一层前缀索引(Term Index),这个索引在Lucene4.0以后采用数据结构FST (Finite State Transducer)。 这种数据结构占用空间很小,Lucene打开索引的时候将其全量装载到内存中,加快磁盘上词典查询速度的同时减少随机磁盘访问次数。
因而每个segment都有会一些索引数据驻留在内存。因此segment越多,占用的内存也越多,并且这部分内存是无法被GC掉的!节点的segment memory的使用情况可以通过如下的方式获取到:
# segment summarized by node
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/segments
# segments summarized by node and index
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/segments?level=indices
# segments summarized by node, index, and shard
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/segments?level=shards
当一个node的segment memory占用过多时,可以通过下面的方法减少segment memory占用:
1. 删除不用的索引。
2. 关闭索引 (文件仍然存在于磁盘,只是释放掉内存)。需要的时候可以重新打开。
3. 定期对不再更新的索引做force merge,可以节省大量的segment memory。
# 强制合并segment为1
POST /{index_name}/_forcemerge?max_num_segments=1
2. Node query cache
Node query cache是用来缓存使用过的filter的结果集。需要注意的是这个缓存也是常驻内存,按照LRU算法进行evict。
# query_cache summarized by node
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/query_cache
# query_cache summarized by node and index
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/query_cache?level=indices
# query_cache summarized by node, index, and shard
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/query_cache?level=shards
Node query cache 由参数控制:
indices.queries.cache.size 默认值10%
index.queries.cache.enabled 默认值true
3. Field Data cache
对搜索结果做排序或者聚合操作,需要将倒排索引里的数据进行解析,按列构造成docid->value的形式才能够做后续快速计算。 对于数据量很大的索引,这个构造过程会非常耗费时间,因此ES 2.0以前的版本会将构造好的数据缓存起来,提升性能。但是由于heap空间有限,当遇到用户对海量数据做计算的时候,就很容易导致heap吃紧,集群频繁GC,根本无法完成计算过程。 ES2.0以后,正式默认启用Doc Values特性,将field data在indexing time构建在磁盘上,经过一系列优化,可以达到比之前采用field data cache机制更好的性能。因此需要限制对field data cache的使用,在mapping设计时关闭了Doc Values 的字段不要进行排序或聚合操作。
节点的Field Data cache的使用情况可以通过如下的方式获取到:
# Fielddata summarized by node
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/fielddata
# Fielddata summarized by node and index
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/fielddata?level=indices
# Fielddata summarized by node, index, and shard
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/fielddata?level=shards
Field Data cache 由参数控制:
indices.fielddata.cache.size 默认值无限制
indices.breaker.fielddata.limit 默认值40%
indices.breaker.fielddata.overhead 默认值1.03
4. Bulk Queue
一般来说,Bulk queue不会消耗很多的heap,但是Bulk Queue设置的较大时,虽然能够应对短暂的请求爆发,但是如果集群本身索引速度一直跟不上, queue都满了会会占用比较多的内存(queue * bulk size)导致内存不足。
Bulk queue 通过如下参数设置:
thread_pool.bulk.queue_size 默认值200,建议不要超过1000
5. Indexing Buffer
Indexing Buffer是用来缓存新数据,当其满了或者refresh/flush interval到了,就会以segment file的形式写入到磁盘。 这个参数的默认值是10% heap size。根据经验,这个默认值也能够很好的工作,应对很大的索引吞吐量。
由如下参数设置:
indices.memory.index_buffer_size 默认值10%,不建议修改
6. Shard Request cache
ES在进行查询时,协调节点将请求发送到分片存在的节点执行,shard级别的缓存请求能够确保频繁的查询快速返回。
# request_cache summarized by node
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/request_cache
由如下参数设置:
indices.requests.cache.size 默认值1%,不建议修改